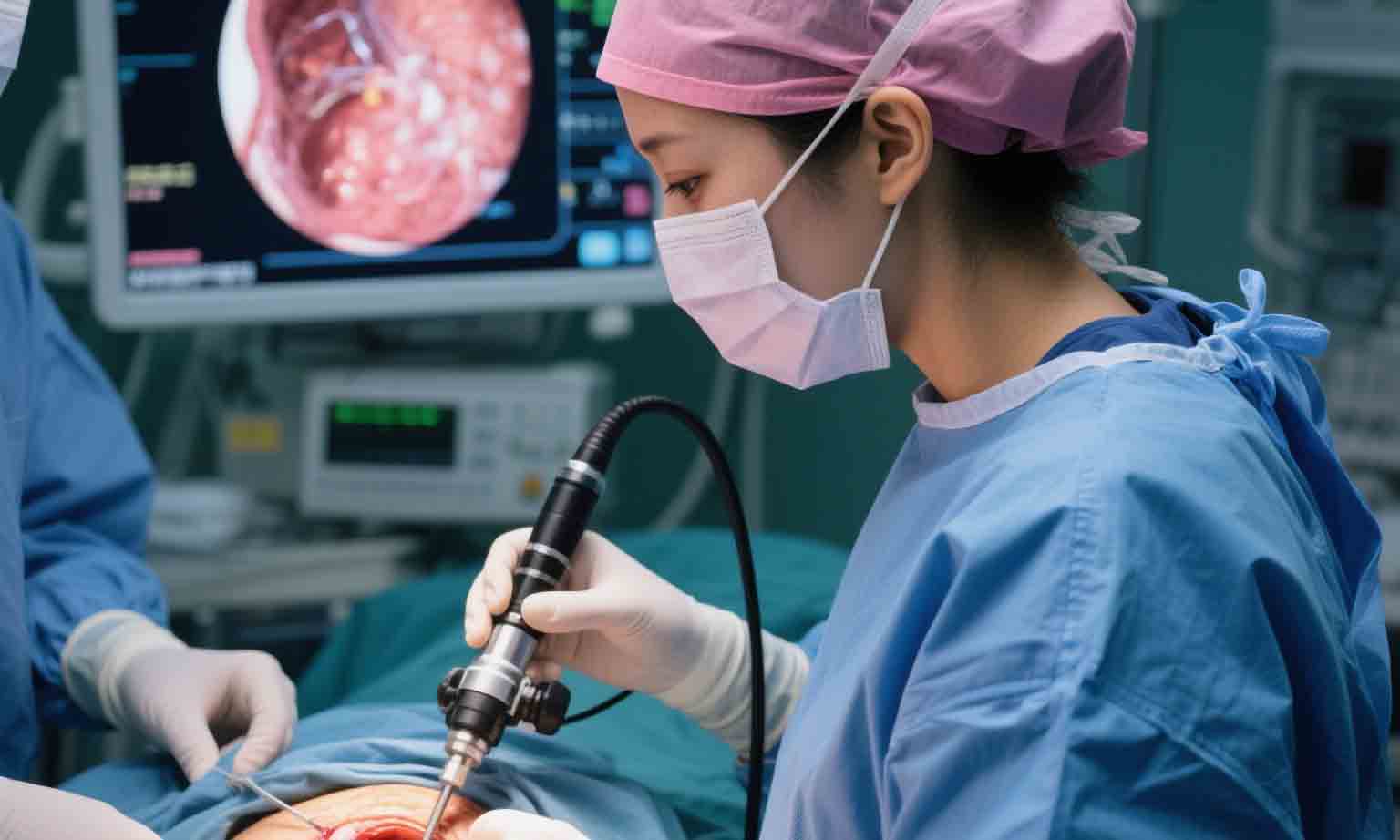
AI in Healthcare – Transforming Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis
gxt 2025-05-28
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated. Early detection is crucial, but in many regions, especially rural or underserved areas, there is a lack of ophthalmologists to screen patients.
Background:
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated. Early detection is crucial, but in many regions, especially rural or underserved areas, there is a lack of ophthalmologists to screen patients.
Solution:
Google Health, in collaboration with hospitals in India and Thailand, developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of detecting referable diabetic retinopathy using retinal fundus photographs. The AI model was trained on a large dataset of eye images labeled by expert doctors.
Implementation:
The AI system was integrated into local clinics where primary care physicians could take retinal photos of diabetic patients and receive immediate analysis from the AI tool. If the system detected signs of retinopathy, the patient was referred to a specialist for further treatment.
Results:
The AI system achieved over 90% accuracy in detecting referable diabetic retinopathy.
It significantly reduced the time required for diagnosis.
More patients in remote areas gained access to early screening and timely treatment.
The workload for specialists decreased, allowing them to focus on more complex cases.
Impact:
This AI application has improved healthcare accessibility and outcomes for diabetic patients. It demonstrates how AI can support medical professionals and bring high-quality diagnostic capabilities to areas with limited resources.
Conclusion:
AI is transforming healthcare by enabling faster, more accurate diagnoses and expanding access to critical services. This case shows just one example of how AI is positively changing lives around the world.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated. Early detection is crucial, but in many regions, especially rural or underserved areas, there is a lack of ophthalmologists to screen patients.
Solution:
Google Health, in collaboration with hospitals in India and Thailand, developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of detecting referable diabetic retinopathy using retinal fundus photographs. The AI model was trained on a large dataset of eye images labeled by expert doctors.
Implementation:
The AI system was integrated into local clinics where primary care physicians could take retinal photos of diabetic patients and receive immediate analysis from the AI tool. If the system detected signs of retinopathy, the patient was referred to a specialist for further treatment.
Results:
The AI system achieved over 90% accuracy in detecting referable diabetic retinopathy.
It significantly reduced the time required for diagnosis.
More patients in remote areas gained access to early screening and timely treatment.
The workload for specialists decreased, allowing them to focus on more complex cases.
Impact:
This AI application has improved healthcare accessibility and outcomes for diabetic patients. It demonstrates how AI can support medical professionals and bring high-quality diagnostic capabilities to areas with limited resources.
Conclusion:
AI is transforming healthcare by enabling faster, more accurate diagnoses and expanding access to critical services. This case shows just one example of how AI is positively changing lives around the world.