The Cutting Edge of AI: Exploring the Latest Advancements
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved at an unprecedented pace over the past decade, revolutionizing industries and reshaping the way we live and work. From natural language processing to autonomous systems, AI continues to push the boundaries of what machines can achieve. This article explores the latest advancements in AI, focusing on key areas such as generative AI, reinforcement learning, AI ethics, and neuromorphic computing.
1. Generative AI and Large Language Models
One of the most transformative developments in recent years has been the rise of generative AI, particularly large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Gemini, and Meta’s LLaMA. These models leverage vast amounts of data and sophisticated neural networks to generate human-like text, images, and even code.
-
Applications: Generative AI is being used in content creation, customer service (chatbots), software development (GitHub Copilot), and even drug discovery.
-
Challenges: Despite its potential, generative AI raises concerns about misinformation, deepfakes, and ethical implications regarding intellectual property and bias.
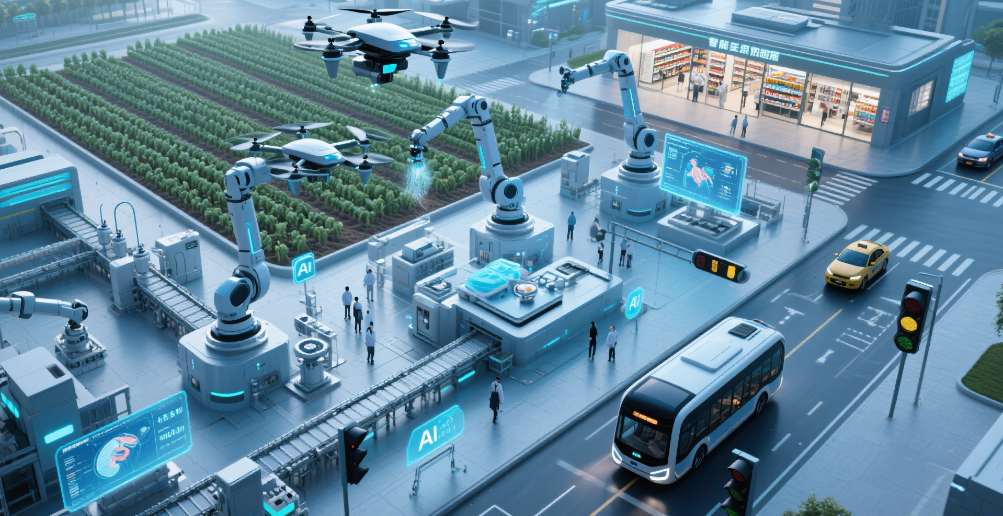
2. Reinforcement Learning and Autonomous Systems
Reinforcement learning (RL)—where AI agents learn by trial and error—has enabled breakthroughs in robotics, gaming, and autonomous vehicles. DeepMind’s AlphaGo and AlphaFold demonstrated how RL can solve complex problems beyond human capability.
-
Advancements:
-
Robotics: AI-powered robots are becoming more adept at real-world tasks, such as warehouse automation (Boston Dynamics) and surgical assistance.
-
Self-Driving Cars: Companies like Tesla and Waymo use RL to improve decision-making in dynamic environments.
-
-
Future Prospects: The next frontier is general-purpose AI robots that can adapt to multiple tasks without retraining.
3. AI Ethics and Responsible AI
As AI becomes more powerful, ethical concerns grow. Issues like algorithmic bias, data privacy, and AI accountability are critical.
-
Explainable AI (XAI): Researchers are developing models that provide transparency in decision-making, crucial for healthcare and legal applications.
-
Regulation: The EU’s AI Act and the U.S. AI Bill of Rights aim to ensure AI is used responsibly.
-
Bias Mitigation: Techniques like fairness-aware machine learning help reduce discrimination in hiring, lending, and law enforcement.
4. Neuromorphic Computing and Brain-Inspired AI
Traditional AI relies on von Neumann architecture, which separates memory and processing. Neuromorphic computing mimics the human brain’s structure, enabling more efficient and adaptive AI.
-
Benefits:
-
Energy Efficiency: Neuromorphic chips (e.g., Intel’s Loihi) consume far less power than conventional GPUs.
-
Real-Time Learning: These systems can learn continuously, making them ideal for edge AI applications.
-
-
Potential Uses: Smart sensors, medical diagnostics, and adaptive robotics.
5. Quantum AI: The Next Frontier
Quantum computing promises to revolutionize AI by solving problems that are currently intractable for classical computers.
-
Quantum Machine Learning (QML): Algorithms like quantum neural networks could accelerate drug discovery, optimization problems, and cryptography.
-
Challenges: Quantum computers are still in early development, with issues like error correction and scalability.
Conclusion
AI is advancing at a breathtaking pace, with innovations in generative models, reinforcement learning, ethical AI, neuromorphic computing, and quantum AI shaping the future. While these technologies offer immense potential, they also pose ethical and societal challenges that must be addressed. As we move forward, interdisciplinary collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders will be essential to harness AI’s benefits responsibly.
The next decade will likely see AI becoming even more integrated into daily life, blurring the lines between human and machine intelligence. The question is no longer if AI will transform the world, but how we will guide its evolution to ensure a beneficial and equitable future.