AI in Agriculture: Cultivating the Future of Sustainable Farming
观棋 2025-06-05
The agricultural sector is undergoing a transformative shift with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), revolutionizing traditional farming practices. From optimizing resource use to enhancing crop yields and ensuring food security, AI technologies are addressing global challenges such as climate change, labor shortages, and increasing demand for sustainable food production. This article explores the pivotal role of AI in modern agriculture, its key applications, challenges, and the promising future it offers.
AI in Agriculture: Cultivating the Future of Sustainable Farming
The agricultural sector is undergoing a transformative shift with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), revolutionizing traditional farming practices. From optimizing resource use to enhancing crop yields and ensuring food security, AI technologies are addressing global challenges such as climate change, labor shortages, and increasing demand for sustainable food production. This article explores the pivotal role of AI in modern agriculture, its key applications, challenges, and the promising future it offers.
1. Precision Agriculture: Data-Driven Decision Making
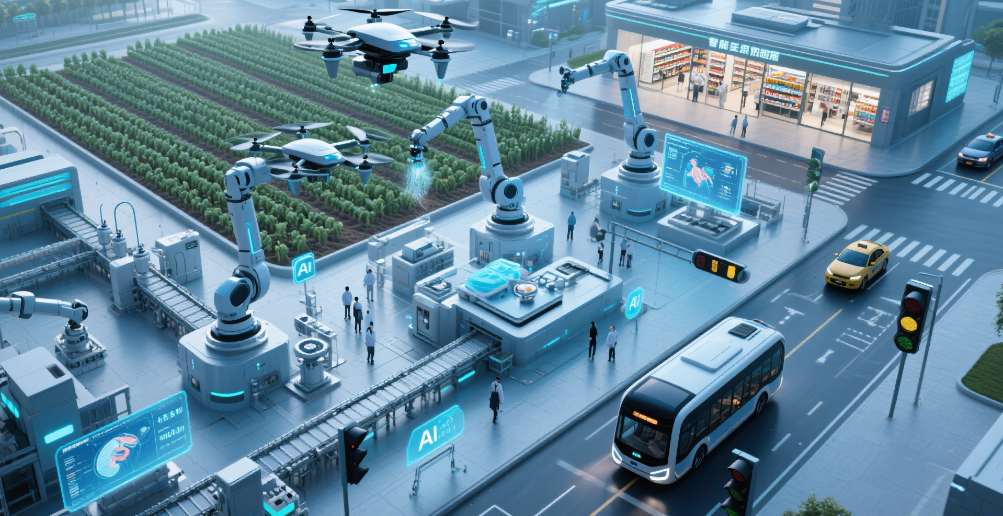
AI lies at the core of precision agriculture, enabling farmers to manage resources with unprecedented accuracy. Sensors, drones, and satellite imagery collect vast datasets on soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop health, which AI algorithms analyze to deliver actionable insights. For example, John Deere’s See & Spray technology uses computer vision and machine learning to identify weeds and apply herbicides only where needed, reducing chemical use by up to 80% while protecting crop quality .
Crop monitoring systems, like those developed by Pioneer Hi-Bred (a Corteva Agriscience brand), leverage AI to detect early signs of stress—such as drought or pest infestations—by analyzing leaf color and texture changes in real time . These systems help farmers intervene proactively, minimizing yield losses. In India, the CropIn platform uses AI to predict optimal planting and harvesting times based on local weather patterns and soil conditions, increasing farm productivity by 15–20% across 5 million acres .
2. Smart Livestock Management
AI is also revolutionizing livestock farming by improving animal health, welfare, and productivity. Wearable sensors and computer vision systems monitor vital signs, feeding habits, and behavioral patterns. For instance, Cowlar collars use AI to detect heat cycles in cows with 95% accuracy, optimizing breeding efficiency and reducing manual labor . Similarly, Agrirouter’s AI-driven platforms analyze milk production data to identify early symptoms of diseases like mastitis, enabling timely veterinary intervention .
In poultry farms, AI-powered cameras from Zedera monitor flock behavior to detect stress or aggression, improving animal welfare and reducing mortality rates by 25% . These technologies not only enhance productivity but also align with global ethical farming standards, addressing consumer concerns about sustainable livestock practices.
3. Predictive Analytics for Crop Yield and Market Trends
AI’s predictive capabilities help farmers anticipate yield outcomes and market demands. Machine learning models, trained on historical data of weather, soil quality, and crop performance, can forecast yields with up to 90% accuracy. Companies like IBM Watson Agriculture offer platforms that combine climate data, satellite imagery, and market trends to guide crop selection and pricing strategies, empowering farmers to make data-driven business decisions .
For smallholder farmers in developing countries, AI-driven apps like FarmDrive in Kenya use mobile data to assess soil fertility and recommend crop varieties, increasing yields by 10–15% for maize and soybean farmers . These tools bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern technology, fostering resilience in the face of climate uncertainty.
4. Autonomous Machinery and Robotics
AI-enabled robots and autonomous vehicles are transforming farm operations, addressing labor shortages and improving efficiency. Blue River Technology (a John Deere company) developed the Harvest Automation HV100, a robot that autonomously harvests soft fruits like strawberries with 95% accuracy, reducing reliance on manual labor . In Japan, Yanmar’s AI-powered tractors use GPS and machine learning to plow fields with centimeter-level precision, even in uneven terrains, cutting fuel consumption by 10% and increasing plowing speed by 20% .
Drones equipped with multispectral cameras, such as those from Parrot Drone, map large fields in minutes, identifying nutrient deficiencies or pest outbreaks. AI algorithms process drone data to generate detailed field maps, guiding targeted interventions and reducing input waste .
5. Sustainable Practices and Resource Efficiency
AI plays a critical role in promoting environmental sustainability by optimizing water, fertilizer, and energy use. Smart irrigation systems, like Netafim’s AI-powered solutions, adjust water delivery based on real-time soil moisture data, reducing water waste by 30–50% in crops like tomatoes and lettuce . AI also helps minimize chemical runoff: Prospera Technologies’s computer vision systems detect plant diseases at the leaf level, enabling precise pesticide application and protecting ecosystems from overexposure .
In vertical farming and controlled-environment agriculture (CEA), AI optimizes lighting, temperature, and CO₂ levels to maximize yields in minimal space. Companies like AeroFarms use machine learning to reduce energy consumption by 50% while growing leafy greens 390 times faster than traditional farms .
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers immense promise, several challenges must be addressed:
Data Access and Privacy: Smallholder farmers often lack access to high-quality data or affordable AI tools, exacerbating the digital divide. Ensuring data ownership and security is crucial, especially as platforms collect sensitive farm information .
Technical Complexity: Integrating AI systems requires technical expertise, which many farmers—particularly in developing regions—lack. User-friendly interfaces and localized training programs are essential for adoption .
Regulatory Frameworks: Standards for AI-driven decision-making in agriculture, such as algorithmic transparency and liability in case of yield failures, are still evolving. Global collaboration is needed to establish ethical guidelines .
Environmental Impact: While AI reduces chemical use, the carbon footprint of data centers and hardware must be minimized to align with sustainability goals .
Future Outlook
The global agricultural AI market is projected to reach $45.2 billion by 2030, driven by innovations in machine learning, IoT, and robotics . Emerging trends include:
AI-Powered Gene Editing: Tools like CRISPR, combined with AI, could accelerate the development of climate-resilient crop varieties, such as drought-tolerant maize or pest-resistant wheat .
Digital Twins for Farms: Virtual replicas of fields or livestock operations will allow farmers to simulate scenarios (e.g., extreme weather) and optimize strategies in real time .
Blockchain Integration: AI-analyzed data paired with blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency, ensuring traceability from farm to consumer and combating food fraud .
Conclusion
AI is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern agriculture, offering solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing challenges. By bridging technology with tradition, AI empowers farmers to grow more with less, protect the environment, and feed a growing global population. As stakeholders invest in innovation, collaboration, and inclusivity, the agricultural sector stands on the cusp of a intelligentre volution—one that promises a more sustainable, resilient, and productive future for all.
This convergence of AI and agriculture is not just about enhancing yields; it’s about redefining the very essence of farming—from a labor-intensive, unpredictable practice to a data-driven, precision science. The journey ahead requires overcoming technical, economic, and ethical hurdles, but the rewards—food security, environmental stewardship, and rural prosperity—are too significant to ignore.
The agricultural sector is undergoing a transformative shift with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), revolutionizing traditional farming practices. From optimizing resource use to enhancing crop yields and ensuring food security, AI technologies are addressing global challenges such as climate change, labor shortages, and increasing demand for sustainable food production. This article explores the pivotal role of AI in modern agriculture, its key applications, challenges, and the promising future it offers.
1. Precision Agriculture: Data-Driven Decision Making
AI lies at the core of precision agriculture, enabling farmers to manage resources with unprecedented accuracy. Sensors, drones, and satellite imagery collect vast datasets on soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop health, which AI algorithms analyze to deliver actionable insights. For example, John Deere’s See & Spray technology uses computer vision and machine learning to identify weeds and apply herbicides only where needed, reducing chemical use by up to 80% while protecting crop quality .
Crop monitoring systems, like those developed by Pioneer Hi-Bred (a Corteva Agriscience brand), leverage AI to detect early signs of stress—such as drought or pest infestations—by analyzing leaf color and texture changes in real time . These systems help farmers intervene proactively, minimizing yield losses. In India, the CropIn platform uses AI to predict optimal planting and harvesting times based on local weather patterns and soil conditions, increasing farm productivity by 15–20% across 5 million acres .
2. Smart Livestock Management
AI is also revolutionizing livestock farming by improving animal health, welfare, and productivity. Wearable sensors and computer vision systems monitor vital signs, feeding habits, and behavioral patterns. For instance, Cowlar collars use AI to detect heat cycles in cows with 95% accuracy, optimizing breeding efficiency and reducing manual labor . Similarly, Agrirouter’s AI-driven platforms analyze milk production data to identify early symptoms of diseases like mastitis, enabling timely veterinary intervention .
In poultry farms, AI-powered cameras from Zedera monitor flock behavior to detect stress or aggression, improving animal welfare and reducing mortality rates by 25% . These technologies not only enhance productivity but also align with global ethical farming standards, addressing consumer concerns about sustainable livestock practices.
3. Predictive Analytics for Crop Yield and Market Trends
AI’s predictive capabilities help farmers anticipate yield outcomes and market demands. Machine learning models, trained on historical data of weather, soil quality, and crop performance, can forecast yields with up to 90% accuracy. Companies like IBM Watson Agriculture offer platforms that combine climate data, satellite imagery, and market trends to guide crop selection and pricing strategies, empowering farmers to make data-driven business decisions .
For smallholder farmers in developing countries, AI-driven apps like FarmDrive in Kenya use mobile data to assess soil fertility and recommend crop varieties, increasing yields by 10–15% for maize and soybean farmers . These tools bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern technology, fostering resilience in the face of climate uncertainty.
4. Autonomous Machinery and Robotics
AI-enabled robots and autonomous vehicles are transforming farm operations, addressing labor shortages and improving efficiency. Blue River Technology (a John Deere company) developed the Harvest Automation HV100, a robot that autonomously harvests soft fruits like strawberries with 95% accuracy, reducing reliance on manual labor . In Japan, Yanmar’s AI-powered tractors use GPS and machine learning to plow fields with centimeter-level precision, even in uneven terrains, cutting fuel consumption by 10% and increasing plowing speed by 20% .
Drones equipped with multispectral cameras, such as those from Parrot Drone, map large fields in minutes, identifying nutrient deficiencies or pest outbreaks. AI algorithms process drone data to generate detailed field maps, guiding targeted interventions and reducing input waste .
5. Sustainable Practices and Resource Efficiency
AI plays a critical role in promoting environmental sustainability by optimizing water, fertilizer, and energy use. Smart irrigation systems, like Netafim’s AI-powered solutions, adjust water delivery based on real-time soil moisture data, reducing water waste by 30–50% in crops like tomatoes and lettuce . AI also helps minimize chemical runoff: Prospera Technologies’s computer vision systems detect plant diseases at the leaf level, enabling precise pesticide application and protecting ecosystems from overexposure .
In vertical farming and controlled-environment agriculture (CEA), AI optimizes lighting, temperature, and CO₂ levels to maximize yields in minimal space. Companies like AeroFarms use machine learning to reduce energy consumption by 50% while growing leafy greens 390 times faster than traditional farms .
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers immense promise, several challenges must be addressed:
Data Access and Privacy: Smallholder farmers often lack access to high-quality data or affordable AI tools, exacerbating the digital divide. Ensuring data ownership and security is crucial, especially as platforms collect sensitive farm information .
Technical Complexity: Integrating AI systems requires technical expertise, which many farmers—particularly in developing regions—lack. User-friendly interfaces and localized training programs are essential for adoption .
Regulatory Frameworks: Standards for AI-driven decision-making in agriculture, such as algorithmic transparency and liability in case of yield failures, are still evolving. Global collaboration is needed to establish ethical guidelines .
Environmental Impact: While AI reduces chemical use, the carbon footprint of data centers and hardware must be minimized to align with sustainability goals .
Future Outlook
The global agricultural AI market is projected to reach $45.2 billion by 2030, driven by innovations in machine learning, IoT, and robotics . Emerging trends include:
AI-Powered Gene Editing: Tools like CRISPR, combined with AI, could accelerate the development of climate-resilient crop varieties, such as drought-tolerant maize or pest-resistant wheat .
Digital Twins for Farms: Virtual replicas of fields or livestock operations will allow farmers to simulate scenarios (e.g., extreme weather) and optimize strategies in real time .
Blockchain Integration: AI-analyzed data paired with blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency, ensuring traceability from farm to consumer and combating food fraud .
Conclusion
AI is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern agriculture, offering solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing challenges. By bridging technology with tradition, AI empowers farmers to grow more with less, protect the environment, and feed a growing global population. As stakeholders invest in innovation, collaboration, and inclusivity, the agricultural sector stands on the cusp of a intelligentre volution—one that promises a more sustainable, resilient, and productive future for all.
This convergence of AI and agriculture is not just about enhancing yields; it’s about redefining the very essence of farming—from a labor-intensive, unpredictable practice to a data-driven, precision science. The journey ahead requires overcoming technical, economic, and ethical hurdles, but the rewards—food security, environmental stewardship, and rural prosperity—are too significant to ignore.